Technology offers of the University of Potsdam
Here you can find current short descriptions of the patent-pending technologies of the University of Potsdam. Our exposés also give an overview of the status of patenting, possible areas of application and exploitation offers (cooperations, licenses, etc.). Many registrations have already been made, some are still being examined by the responsible authorities.
Do not hesitate to contact us with any questions or requests. We are happy to assist you in contacting the respective inventors.
This page is constantly updated, so repeat visits can be worthwhile! In the near future you will also find our offers in the Invention Store on the website of TransferAllianz, the German Association for Knowledge and Technology Transfer.
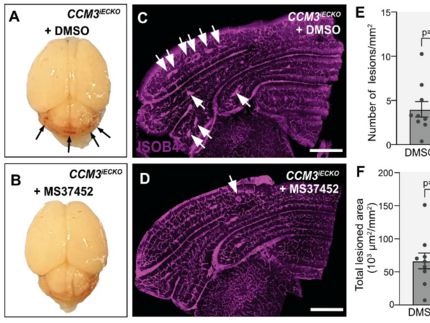
Treatment of cerebral cavernous malformations with CBX7 inhibitors
(Ref. 21-01)
Inventor: Prof. Dr. Salim Seyfried
The method according to the invention relates to a novel pharmacological approach for combating severe cerebrovascular diseases and is based on inhibitors of CBX7, a component of the polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1).
Patent status: European unitary patent (07-2024 granted)
Exposé 21-01 (german, PDF | 1,18 MB)
EP 4 154 876 B1 (PDF | 1,12 MB)
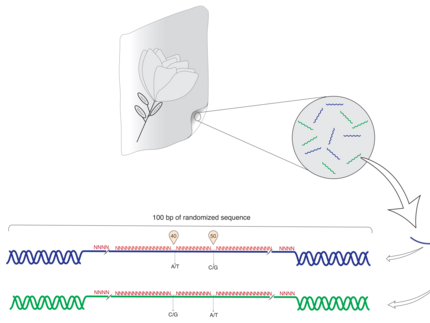
DNA-Tagging
(Ref. 21-03)
Inventors: Prof. Bernd Müller-Röber, Dr. Lena Hochrein, Ali Tafazoli Yazdi
The method according to the invention is used for forgery-proof molecular labelling of valuable products or objects and is based on encoded nucleic acids.
Patent status: EP pending, US pending
Exposé 21-03 (german, PDF | 371 KB)
WO/2023/139011 (PDF | 3,09 MB)
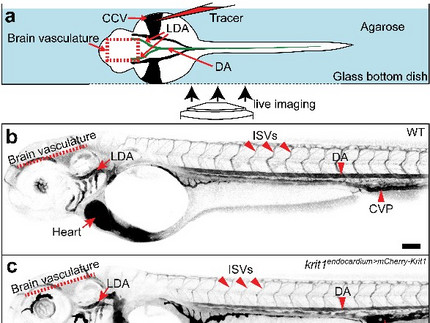
Zebrafish stroke model
(Ref. 19-04)
Inventors: Prof. Dr. Salim Seyfried, Dr. Claudia Rödel
The present invention is a genetic system in the vertebrate model zebrafish embryo, which enables the analysis of disease-relevant conditions of the blood vessel disease cerebral cavernous malformations (CCM) under blood flow conditions. In this way, pharmacological effects on the formation of disease-related blood vessel changes can be investigated.
Patent status: EP granted (validated in DE)
Exposé 19-04 (german, PDF | 845 KB)
EP3782465B1 (PDF | 8 MB)
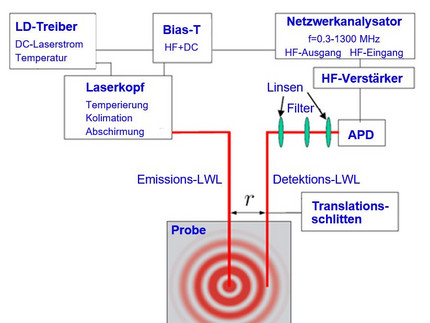
PDW spectroscopy
(Ref. 06-38)
Inventors: Prof. Dr. Hans-Gerd Löhmannsröben, Dr. Oliver Reich
The measuring arrangement according to the invention is based on the generation and detection of photon density waves in nanoheterogeneous, highly light-scattering materials to determine their absorption and scattering properties. This makes the observation of a large number of chemical reaction processes (e.g. emulsion polymerisation) very accessible.
Patent status: EP granted (validated in DE), US granted
Exposé 06-38 (german, PDF | 327 KB)
EP 2040050 (PDF | 268 KB)
US 8,339,599 (PDF | 78,7 KB)
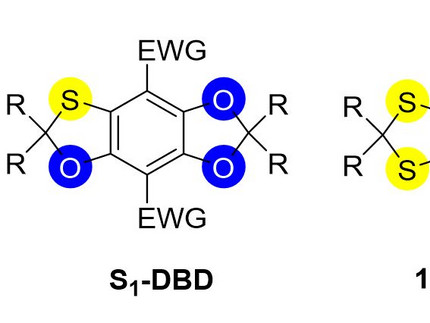
Thiopolyphenol fluorescent dyes
(Ref. 19-15)
Inventors: Prof. Dr. Pablo Wessig, Leonard John
These novel fluorescent dyes, which are based on oxygen- and sulphur-containing heterocycles, represent a further development of the [1,3]-dioxolo[4.5-f]benzodioxole (DBD) dyes, whereby one or two oxygen atoms of the DBD scaffold have been replaced by sulphur atoms. These structural changes lead to a significant improvement in photophysical properties compared to the previously developed S4 DBD dyes. Please also note the offer 17-02.
Patent status: DE pending
Exposé 19-15 (german, PDF | 250 KB)
DE 10 2020 114 139 A1 (PDF | 774 KB)
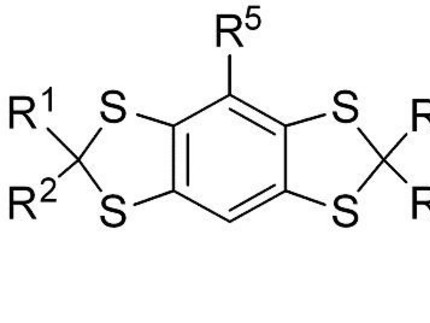
Fluorescent dyes with 2-photon absorption capability
(Ref. 17-02)
Inventors: Prof. Dr. Pablo Wessig, Daniel Freyse
The present invention involves novel fluorescent dyes that have better hydrolytic stability, higher excitation and emission wavelengths and larger Stokes shifts compared to already known fluorescent dyes with a similar basic structure. In addition, they have high bleaching stability and better synthetic accessibility. Please also note the offer 19-15.
Patent status: DE granted
Exposé 17-02 (german, PDF | 292 KB)
DE 10 2017 122 275 (PDF | 271 KB)
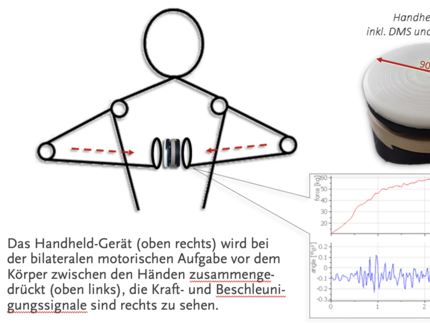
Regulation of muscle and tendon oscillation
(Ref. 14-24)
Inventors: Prof. Dr. Frank Bittmann, Dr. Laura Schaefer, Stefanie Venner-Zinn
The present invention is a device for the individualised feedback regulation of muscle and tendon oscillations during various forms of muscle action or training - in particular for use in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's syndrome. The aim and new feature is to re-train the physiological oscillation patterns in order to achieve a positive effect on the symptoms and progression of the disease.
Patent status: DE granted
Exposé 14-24 (german, PDF | 654 KB)
DE 10 2015 119 741 B4 (PDF | 614 KB)
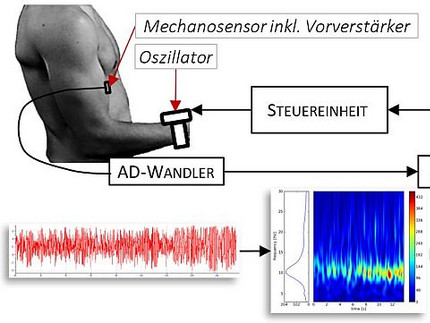
Handheld device for recording neuromuscular functions
(Ref. 18-02)
Inventors: Prof. Dr. Frank Bittmann, Dr. Laura Schaefer
The device according to the invention records the reaction force between the extremities and the oscillations generated by the muscles simultaneously over time. The technology could be of significance for the diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases (e.g. Parkinson's syndrome).
Patent status: DE pending
Exposé 18-02 (german, PDF | 629 KB)
DE 11 2020 001 149 (PDF |3 MB)
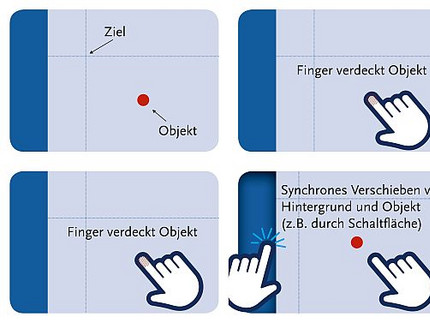
Precise positioning on touchscreens
(Ref. 15-01)
Inventors: Prof. Dr. Ulrich Kortenkamp, Heiko Etzold, Christian Dohrmann
Touch-sensitive screens (touchscreens) have the problem that, during operation, exactly those objects on the screen with which an interaction is to take place are covered. With the present invention, a user action moves the entire screen area or a meaningful sub-area far enough away under the finger so that the previously covered area is visible again. By moving the finger, the selected object can now be moved as desired and positioned exactly. The previously hidden area remains fully visible.
Patent status: DE granted
Exposé 15-01 (german, PDF | 339 KB
DE 10 2015 107 262 (PDF | 157 KB)
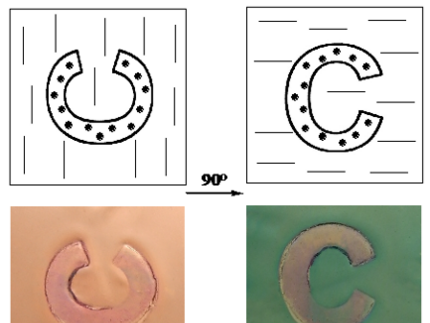
Optically anisotropic security features
(Ref. 12-27)
Inventors: Dr. Jana Bomm, Dr. Joachim Stumpe
According to the invention, optically anisotropic polymer nanocomposite films or fibres can be chemically integrated into cellulose-based compositions such as banknotes, documents or packaging, thus forming a new type of security label.
Patent status: DE granted
Exposé 12-27 (german, PDF | 341 KB)
DE 10 2013 109 002 (PDF | 605 KB)