Verwendete Methoden
Spektroskopie
IR-Spektroskopie
Aufnahme von IR-Spektren in Transmission mit KBr- bzw. CsI-Pressling (4000-500 cm⁻¹ bzw. 1000-80 cm⁻¹) bzw. abgeschwächte Totalreflexion mit ATR-Einheit mit Diamant- bzw. ZnSe-Kristall (30000-200 cm⁻¹ bzw. 20000-500 cm⁻¹)
Elektrochemie
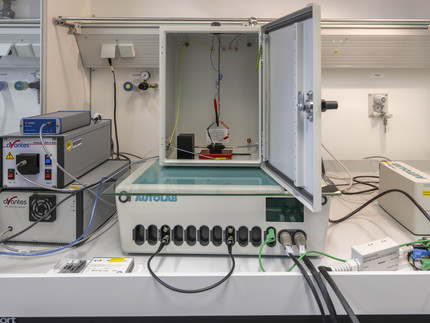
Cyclovoltammetrie
Bestimmung von Redoxpotentialen in organischen Lösemitteln oder wässriger Lösung
Metrohm Autolab Potentiostat/Galvanostat mit 4 mL-Zelle (Platin-Gegenelektrode, Glassy-Carbon-Arbeitselektrode, wahlweise Ag/AgCl-Referenzelektrode (wässrig) oder Ag/AgNO₃-Referenzelektrode (organisch, Ar-Schutzgasatmosphäre möglich), unten rechts: Metrohm DropSens μStat 400 Bipotentiostat/Galvanostat mit Chipelektroden (nur wässrig)
Elementanalytik
Sonstiges
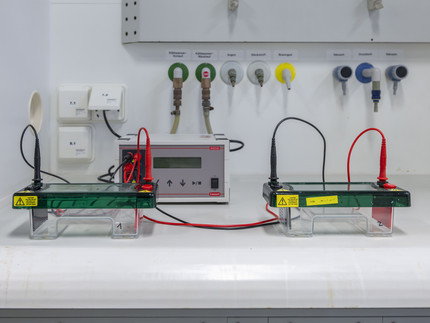
Gelscanner
Visualisierung und Quantifizierung von Gelelektrophorese-Experimenten mit verschiedenen Einsätzen (Trays) je nach Gelfärbe-Methode:
- UV Sample Tray (für Bestrahlung mit UV-Licht)
- Stain-free Sample Tray (für ungefärbte Gele)
- White Sample Tray (Coomassie Blau-, Kupfer-, Silber-, Zink-Färbung)
Synthese
- Organische Synthese und Koordinationschemie, teilweise unter Inertgasatmosphäre
- Reaktionen im Parallelsynthesereaktor im kleinen Maßstab (mit Bestrahlung möglich)
- Festphasenpeptidsynthese und Biokonjugatchemie