Biological role of nonribosomal peptides in Microcystis
Background
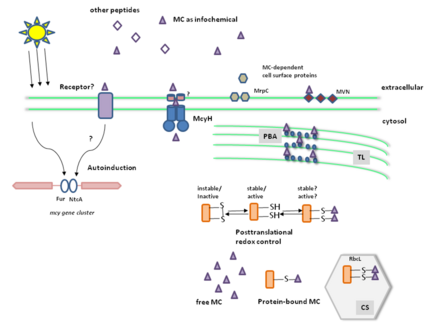
Microcystin is a cyanobacterial toxin that causes a serious threat to drinking water and recreational lakes worldwide. As part of our ongoing study we could show that microcystin fulfils an important function within cells of its natural producer Microcystis. We have performed a global proteomic comparison with extracts of the microcystin producing wild type strain PCC7806 and the mcyB mutant. The microcystin deficient mutant mcyB showed significant changes in the accumulation of proteins, including several enzymes of the Calvin cycle, phycobiliproteins and two NADPH-dependent reductases. Coincidently, we have discovered that microcystin binds to a number of these proteins in vivo. The nature of the binding was studied using extracts of a microcystin-deficient mutant in vitro. As a result, we have found clear evidence for a covalent interaction of the toxin with cysteines of proteins. The microcystin binding to proteins is strongly enhanced under conditions triggering oxidative stress. Correspondingly, the mcyB mutant defective in microcystin production exhibited an increased sensitivity towards oxidative stress conditions. We have further discovered a role of microcystin as infochemical and a strong influence of the toxin on the expression of cell surface proteins. Taken together, our data suggest a redox-dependent, protein-modulating role for microcystin within the producing cell, which represents a new addition to the catalogue of functions that have been discussed for microbial secondary metabolites.
Publications
Schuurmans J.M., Brinkmann, B.W., Makower, A.K., Dittmann, E., Huisman, J., Matthijs, H.C.P. (2018) Microcystin interfers with defense against oxidative stress in harmful cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 78: 47-55.
Hackenberg, C., Hakanpää, J., Cai, F., Antonyuk, S., Eigner, S., Meissner, S., Laitaoja, M., Jänis, J., Kerfeld, C.A., Dittmann, E., Lamzin, V.S. (2018) Structural and functional insights into the unique CBS-CP12 fusion protein family in cyanobacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115: 7141-7146
Hu, C., Ludsin, S.A., Martin, J.F., Dittmann, E., Lee, J (2018) Mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs)-producing Microcystis in Lake Erie: Development of a qPCR assay and insight into its ecology Harmful Algae 77:1-10.
Woodhouse, J.N., Makower, A.K., Grossart, H.P., Dittmann, E. (2017) Draft genome sequence of two uncultured Armatimonadetes associated with a Microcystis sp. (cyanobacteria) isolate. Genome Announc. 5 (40): pii: e00717-17
Pearson, L.A., Dittmann, E., Mazmouz, R., Ongley, S.E., D'Agostino, P.M., Neilan, B.A. (2016) The genetics, biosynthesis and regulation of toxic specialized metabolites of cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 54: 98-111.
Makower, K., Schuurmans, J.M., Groth, D., Zilliges, Y., Matthijs, H.C.P., Dittmann, E. (2015) Transcriptomics aided dissection of the intracellular and the extracellular role of microcystin in M. aeruginosa PCC 7806. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 81:544-554.
Hu, C., Völler, G., Süßmuth, R., Dittmann, E., Kehr, J.C. (2015) Functional assessment of mycosporine-like amino acids in Microcystis aeruginosa strain PCC7806. Environ. Microbiol., doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12577
Meissner, S., Steinhauser, D., Dittmann, E. (2015) Metabolomic analysis indicates a pivotal role of the hepatotoxin microcystin in high light adaptation of Microcystis. Environ. Microbiol., DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.12565
Voß, B., Bolhuis, H., Fewer, D.P., Kopf, M., Möke, F., Haas, F., El-Shehawy, R., Hayes, P., Bergman, B., Sivonen, K., Dittmann, E., Scanlan, D.J., Hagemann, M., Stal, L.J., Hess, W.R. (2013) Insights into the physiology and ecology of the brackish-water-adapted cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena CCY9414 based on a genome-transcriptome analysis. PLoS One doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060224.
Kehr, J.C., Dittmann, E. (2013) Cyanobakterielle Toxine: Von der Biosynthese zur Funktion. Biospektrum 19: 16-18.
Meissner, S., Fastner, J., Dittmann, E. (2013) Microcystin production re-visited: Conjugate formation makes a major contribution. Environ. Microbiol. 15: 1810-1820.
Dittmann, E., Fewer, D., Neilan, B.A. (2013) Cyanobacterial Toxins: Biosynthetic Routes and Evolutionary Roots. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 37: 23-43.
Neilan, B.A., Pearson, L.A., Muenchhoff, J., Moffitt, M.C., Dittmann, E. (2013) Environmental conditions that influence toxin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 15:1239-1253.
Zilliges, I., Kehr, J.C., Meissner, S., Ishida, K., Mikkat, S., Hagemann, M., Kaplan, A., Börner, T., Dittmann, E. (2011) The cyanobacteriel hepatotoxin microcystin binds to proteins and increases the fitness under oxidative stress conditions. PLoS One 10.1371/journal.pone.0017615
Zilliges, Y., Kehr, J.C., Mikkat, S., Bouchier, C., Tandeau de Marsac, N., Börner, T., Dittmann, E. (2008) An extracellular glycoprotein is implicated in cell-cell contacts in the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. J. Bacteriol. 190: 2871-2879.
Schatz, D., Keren, Y., Vardi, A., Sukenik, A., Carmeli, S., Börner, T., Dittmann, E. and Kaplan, A. (2007) Towards clarification of the biological role of microcystins, a family of cyanobacterial toxins. Environ. Microbiol. 9: 965-970.
Kehr, J.-C., Zilliges, Y., Disney, M.D. Ratner, D.M. Bouchier, C., Seeberger, P.H., Tandeau de Marsac, N., Dittmann, E. (2006) A mannan-binding lectin is involved in cell-cell attachment in a toxic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 59: 893-906.
Tonk, L., Visser, P.M., Christiansen, G., Dittmann, E., Weijerman, M., Snelder, E.O.F.M., Wiedner, C., Mur, L.R., Huisman, J. (2005) The cyanobacterium Planktothrix agardhii changes its microcystin composition towards a more toxic variant with increasing irradiance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 71: 5177-5181.
Kaebernick, M., Dittmann, E., Börner, T., Neilan, B.A. (2002) Transcriptional analysis of the microcystin synthetase gene cluster in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa, Appl. Environ. Microbiol, 68: 449-455.
Hesse K, Dittmann E, Börner T (2001) Consequences of impaired microcystin production for light-dependent growth and pigmentation of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 37: 39-43
Kaebernick, M., Neilan, B.A., Börner, T and Dittmann, E. (2000) The effect of light on the regulation of microcystin biosynthesis genes, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66:3387-3392